What Is Cash On Delivery & How Does It Work?

by
Alisa Cvilij
May 17, 2024
The delivery industry uses many forms of payment. From cash payments to credit cards and checks - there are different ways of handling charges depending on the company's payment policy.
When considering different payment methods, the question is not what but when. That is, the payment either happens in advance or at the time of delivery. In other words, Cash in Advance vs Cash on Delivery (COD).
Cash on Delivery has gained immense popularity in several Southeast Asian countries.
This is because the people there have limited access to credit cards which makes COD a game-changer for businesses in these countries. It also allows the customers to trust the online business. The COD market is expected to reach $578.4 billion by 2025, a report by Statista revealed.
In this post, we dive deeper into the COD payment method. What does Cash on Delivery mean, how does it work, and what are its pros and cons for a delivery operation?
Let's roll.
Table of contents
What does Cash on Delivery mean?
The easiest way to think about COD is to picture a pizza delivery where the courier expects a cash payment upon arrival. This same model can be applied to other delivery scenarios.
With Cash on Delivery, a logistics company will accept a cash, check, or credit card payment at the location of delivery rather than in advance.
While Cash in Advance is the most widely used payment method in eCommerce logistics today, some small businesses choose to use COD for all the various benefits that come with it (more on that later).
Larger companies may find it harder to offer Cash on Delivery as a payment method due to more complex accounting procedures.
In short, COD Delivery is now a widely accepted payment method, which the customer prefers when shopping from a new retailer.
With COD delivery, the customer can pay for the products at their doorstep with cash.
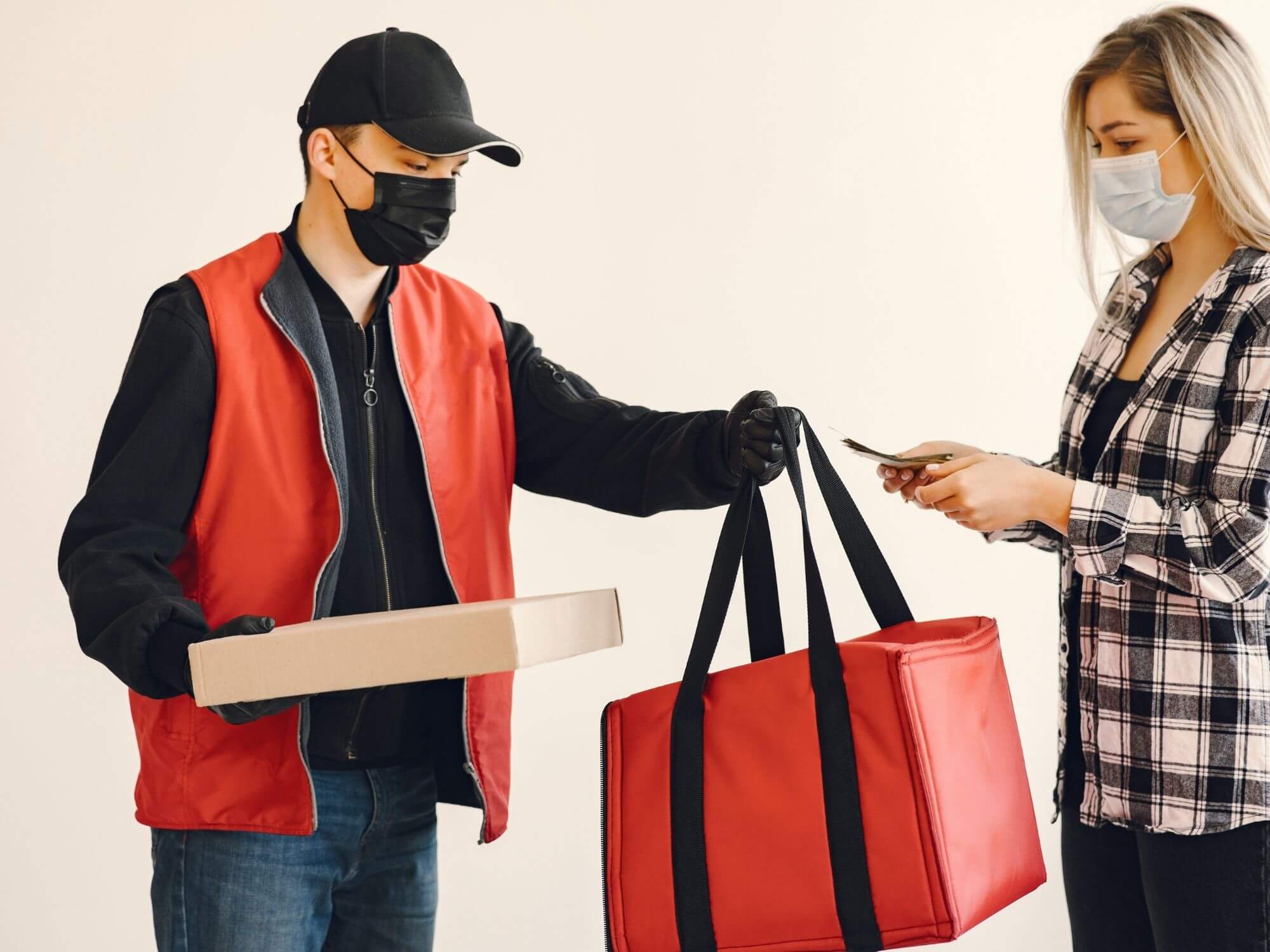

How does Cash on Delivery work?
Now that we know what Cash on Delivery means, let's take a look at how it works in practice.
COD is a payment option used by courier companies and in-house delivery teams alike. Ecommerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce even have dedicated COD setups.
In WooCommerce, for example, merchants can apply Cash on Delivery to any of their shipping methods as well as extend it to virtual orders that don't require shipping but still need to be paid for.
Because COD orders come with higher risks, Shopify lets the stores set a price range that works as a qualification for Cash on Delivery.
If an order costs more than the specified maximum, it simply won't qualify for COD. Therefore, the merchant's risks of shipping without payment are minimized.
Cash on Delivery Example
Cash on Delivery is now being offered by various industries. These industries include:
- eCommerce: Many online shops, like Amazon and Flipkart, let you pay with cash when your order arrives.
- Food delivery: Uber Eats and DoorDash let you pay cash for your food at delivery, especially where few people use digital payments.
- Pharmacies: Online pharmacies often use COD too. Customers can pay for their medicines and health products in cash upon delivery.
Pros and cons of Cash on Delivery
Since we started talking about risks associated with the COD payment method, let's also look at the benefits that come with it.
+ More options for customers
If there's one thing that remains true for eCommerce shipping, it's that more options equals better business.
On this blog, we've spoken multiple times about all the different delivery options. Same-day delivery, contactless delivery, and especially free delivery is what customers expect and will always opt for.
The same goes for payment methods. The more you can offer, the better for the customer. Cash on Delivery in particular provides more security for the buyer.
- The customer feels safer because the risk of fraud is lower.
- There's more time to complete the payment.
- The customer doesn't have to use their credit card if they wish not to.
- Greater risks for the business
Naturally, more options for the customer comes with greater risks for the business.
Online stores that collect on delivery run the risks of payments not being received in full or at all. In this case, shipping costs aren't reimbursed and therefore need to be optimized in advance.
For example, route optimization software used by logistics companies considers all delivery parameters and constraints to build the fastest, cheapest routes, including load planning that helps reduce mileage and save on fuel and driver time.

The silver lining
It's not all risks and no wins for sellers who offer Cash on Delivery. For one, smaller businesses without great brand recognition can use COD to build trust in their delivery services.
While bigger logistics operations may struggle with Cash on Delivery, smaller sellers can embrace COD and use it as an incentive for customers to buy from new places knowing that they have more time to make the payment.
Add to that advanced delivery notifications, dynamic ETA, and live package tracking - and even a small in-house delivery operation can nail self-service and exceed customers' expectations.
In addition to that, Cash on Delivery can be better than credit because you receive the payment in full. In terms of accounting, COD shortens the days receivable, i.e. the short-term debt can be closed faster.
Is Cash on Delivery right for me?
As you can see, there are pros and cons to offering COD as a payment method. As a local delivery operation with in-house staff, you might want to give Cash on Delivery a try and see what it does to your sales and revenue.
The good news is, trying out Cash on Delivery doesn't require big investments. With the right delivery management system, you can incorporate COD with no additional costs.
Moreover, in today's tech-driven world there is a wide variety of technology available to support COD. This allows you to choose the best cash on delivery apps that are best suited to optimize your business operations.
Take Track-POD proof of delivery software as an example. It's a two-part system - a web dispatcher dashboard and a mobile driver app - that builds and optimizes routes and gives your staff the tools to execute paperless & contactless deliveries and pickups.
Cash on Delivery is a feature available in the Track-POD delivery driver app. When creating or importing an order, a COD amount is specified by the dispatcher.
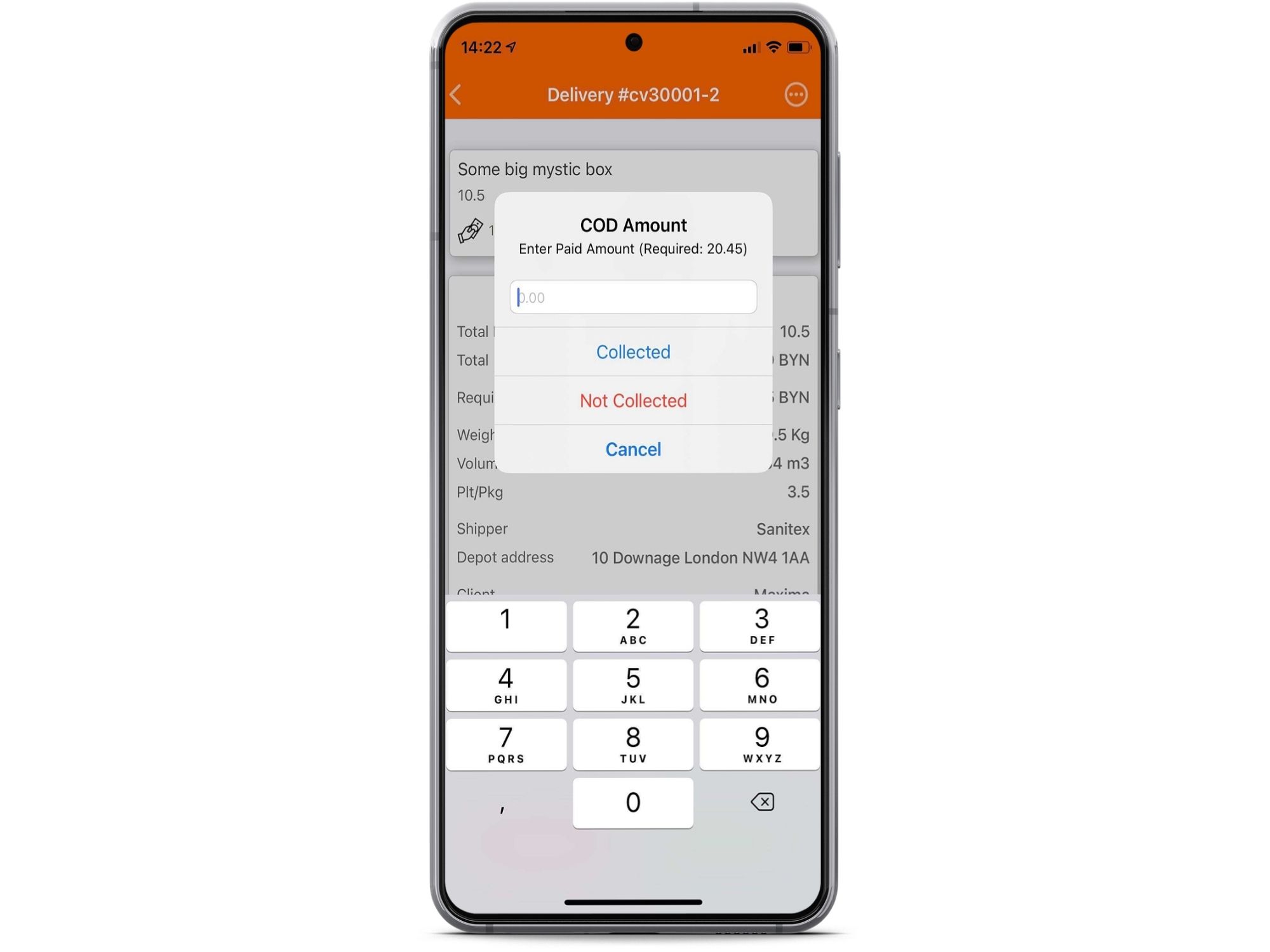
The driver then needs to collect the payment and enter the exact same amount into the app for the job to be completed. E-signature and photos can also be taken for an electronic Proof of Delivery (ePOD) document to be generated automatically.
Countries using COD Payments
COD has become a popular payment option for e-commerce transactions in many countries. These include India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and other less technologically developed countries.
The reason? People in these countries don't have access to credit cards. This forces them to pay for their purchases in cash upon delivery.
However, in countries such as the UK, US, Sweden, Norway, and Singapore, digitalization is prevalent and electronic payment methods are widely adopted. In these countries cash on delivery services are less common due to the preference for digital transactions.
How to do Cash On Delivery securely for your business?
To ensure a safe COD transaction between your consumers and your business, you need to set some policies and guidelines. These policies could include:
- Verify customer's information: First, it is absolutely necessary to verify the customer's information. You can also make a confirmation call to decrease your return rates. The things you need to verify is whether contact information, address and name are legitimate or not.
- Provide accurate delivery date: You need to ensure that you provide the exact delivery range. This also increases the customer retention. You can partner with a fast and reliable cash on delivery courier to make this a smooth experience for yourself and your customers.
- Set a COD purchase value: This policy will ensure that your customers can only buy products that can be paid via COD service. It helps reduce the risk of you losing a significant amount of money if something goes wrong during delivery.
Recap
Cash on Delivery is a payment method that stands in opposition to Cash in Advance. Instead of using credit, sellers collect the payment on location after the order has been delivered.
COD has its pros and cons - both for the customer and the business. While it may be challenging for a big operation, small businesses can benefit from Cash on Delivery as it entails fewer risks for the buyer and helps build trust.
If you're thinking about implementing COD in your shipping workflow, try Track-POD delivery management system that comes with a Cash on Delivery app for the driver. Start your free trial today, no credit card required.
About The Author
Alisa Cvilij
Content Marketer at Track-POD. Passionate about building meaningful and helpful content for the readers.