Crowdsourced Delivery in Last Mile: Challenges, Benefits, and Use Cases

by
Alina Kostukova
August 23, 2023
The gig economy has transformed the last mile industry.
The concept of crowdsourced delivery, or crowdshipping, has stepped into the spotlight as a dynamic solution for transportation management.
With the rise of crowdsourced delivery apps, this logistics strategy is rewriting the rules of the game.
Let's go further into the benefits, challenges, and use cases of crowd logistics for businesses.
What is crowdsourced delivery?
Crowdsourced delivery is a modern operations strategy that uses a network of independent individuals, or contract drivers, to perform the final stage of the delivery process.
This method uses technology, like specialized crowdsourced delivery apps, to connect companies or people who need logistics services with a flexible group of drivers.
At its core, crowdsourced last mile delivery is a groundbreaking approach that taps into the power of community collaboration and modern technology.
This last mile optimization strategy improves cost-effectiveness and supply chain agility by providing quick and efficient delivery solutions.

The role of contract drivers in crowdshipping
Central to the success of crowdshipping are the contract delivery drivers who make it all happen.
Crowd logistics reunites community delivery drivers, contract drivers, and local couriers under the same umbrella.
These drivers operate part-time or freelance, which allows them to choose delivery assignments according to their availability and personal preferences.
Independent contractors bring their own vehicles, i.e. operate a grey fleet and choose delivery shifts based on availability, granting them the autonomy to tailor their work schedules.
These contractors offer businesses the advantage of a flexible and scalable workforce.
Benefits of crowdsourced delivery
Crowdsshipping can be beneficial in a number of ways. Let's discuss the main benefits of this last mile optimization strategy.
1. Cost-effectiveness
Crowdsourced delivery methods allow companies to save costs using a network of independent contract drivers and, often, their vehicles.
Traditional delivery strategies demand significant fleet maintenance and management investments, while crowdsourced distribution reduces fixed overhead costs.
By paying only for completed deliveries, businesses can prevent the financial burden of idle resources during low demand.
2. Effortless and swift setup
The ease and speed of setting up crowd logistics systems are critical. This is especially true for small business owners and people just starting with business logistics.
Small businesses with just a few daily deliveries can benefit from hiring a single local driver for that specific job.
Independent drivers can pick up and deliver a parcel quickly and effectively without any extra paperwork.
Third-party logistics (3PL) and fourth-party logistics (4PL) services cannot provide this flexibility and are often more expensive than crowdsourced shipping services.
Pro tip: In Track-POD, you can easily add and remove new part-time drivers - as the number of vehicles is unlimited with our per-order plans. When hiring a contract driver, you can create their account and share login details so they can set up a driver app in just a few clicks.
3. Eco-friendly impact
In an environmentally concerned age, crowdsourced shipping has become an eco-friendly last mile option.
Reduced distances, better route planning, and aggregation of multiple deliveries translate into a smaller carbon footprint.
4. Customer-centric experience
Crowdshipping apps foster a sense of reliability and connection that can be hard to replicate in traditional delivery models.
Another defining feature that makes crowdsourced delivery a customer-centric experience is the potential for lower cost per mile.
As businesses streamline their delivery operations through crowdsourced networks and independent contract drivers, their running costs decrease. This means that prices for customers go down as well.
Last mile delivery crowdsourcing offers customers flexibility, visibility, and extra speed.
Pro tip: You can use delivery management software, like Track-POD, to track part-time drivers. Track-POD provides tools to send live tracking links and delivery notifications to your customers for enhanced transparency.
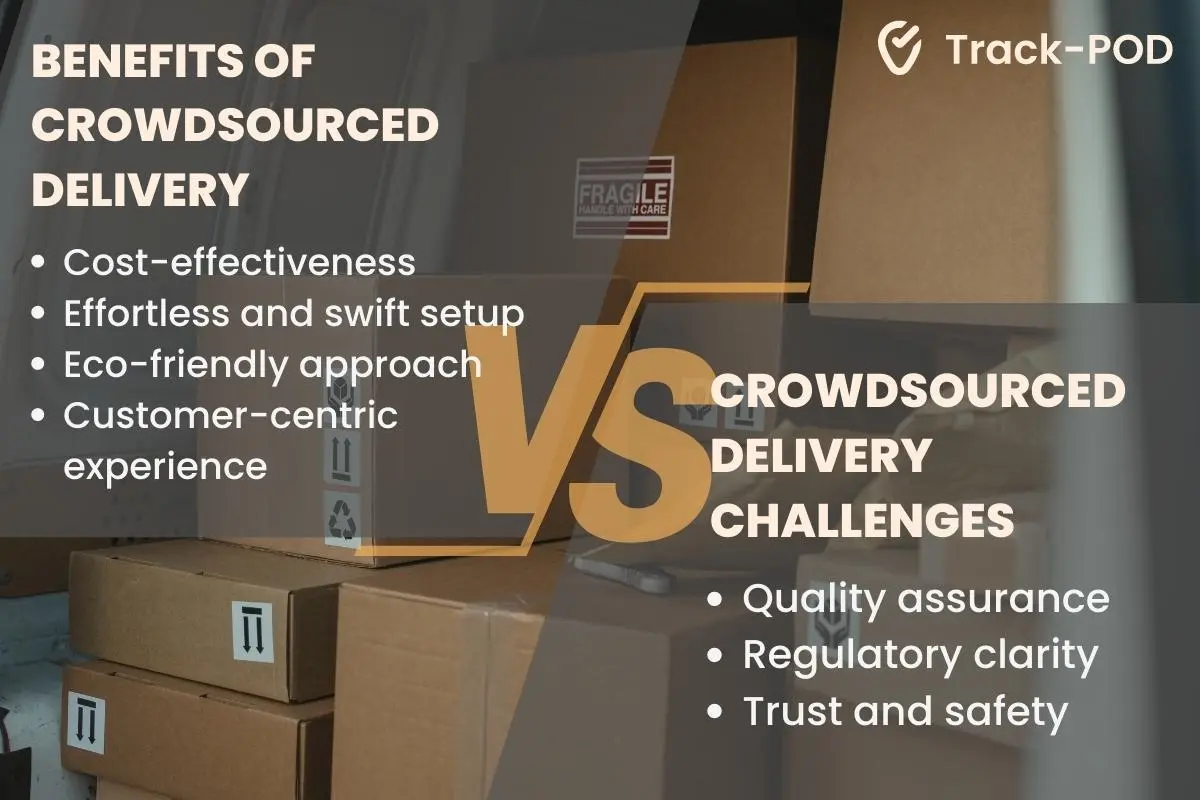
Crowdsourced delivery challenges
Like any last mile optimization strategy, crowdsourced delivery services hide some drawbacks that can impact your business.
Let's discuss the main challenges of this delivery method that warrant attention.
Quality assurance
Maintaining a high standard of service across a distributed network needs careful management.
In case of any issues with last mile delivery, customers will associate them with your brand directly.
For this reason, brand reputation risks are always present when it comes to crowdsourced delivery.
When hiring part-time contract drivers, companies can include these quality assurance guidelines in the contract. Practical training, performance tracking, and feedback mechanisms are vital to maintaining standards.
When it comes to P2P and crowdsourcing networks, it's harder to keep track of quality standards because the platforms themselves set them.
Pro tip: Using last mile delivery software when hiring part-time drivers can bring more control over the quality of their work. In Track-POD Web 2.0, you can easily track driver statuses and idling time. It will help make sure that contract drivers stick to the plan and make the best use of your resources.
Regulatory clarity
The gig economy of contract delivery drivers has raised questions about employment, insurance, and taxes. It has brought up concerns regarding the legal classification of contract drivers.
The question of whether they are independent contractors or employees has far-reaching consequences.
The balance between freedom and protection for contract drivers is challenging for many businesses.
Trust and safety
Crowdshipping delivery services face trust and safety issues.
Technology has made companies, drivers, and customers more connected. Despite that, securing this ecosystem is crucial.
Delivery crowdsourcing raises worries regarding contract driver screening and background checks.
Employing secure payment systems, robust identity verification, proof of loading and delivery processes, and transparent communication channels, all help to build trust between businesses and contract drivers.
Pro tip: Proof of delivery apps help to eliminate paperwork and simplify the delivery confirmation process. By adding photo proof, geostamp, or custom notes, freelance drivers can easily confirm their deliveries.
Types of crowdsourced delivery
Crowdsourced delivery is a broad field with many different ways to do things that fit different needs. Drivers can be employed via specialized platforms that we'll discuss below or on an individual part-time contract basis.
Let's talk about some of the most common types of crowd logistics.
1. Peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms
P2P platforms connect people who need community delivery services with people already traveling to the destination.
This approach ensures that items find their way to recipients via the existing routes.
This reduces the carbon footprint and makes the method more sustainable.
2. On-demand delivery
People and companies can ask for instant delivery services with on-demand community delivery apps.
Contract delivery drivers or local couriers nearby can accept these assignments, resulting in prompt and efficient delivery.
3. Crowdshipping networks
Building on the sharing economy, crowdshipping networks consist of a verified community of "occasional couriers" or gig workers who offer their services for a fee.
In simple terms, crowdshipping networks are created for businesses to find local couriers or professional delivery drivers willing to work part-time.
4. Locker-based solutions
Some crowdshipping apps leverage secure locker systems strategically placed in easily accessible locations.
This ensures even more flexible delivery options as contract drivers or regular commuters can drop off packages, and recipients can retrieve them whenever suits them best.
5. Micro-fulfillment centers
In urban areas, micro-fulfillment centers act as efficient hubs for crowdsourced delivery.
Contract drivers can pick up goods at these centers and make multiple trips within a certain radius, making the best use of their routes and speeding up the process.

Wrapping up
Crowdsourced delivery, or crowd logistics, has evolved as a dynamic delivery alternative, transforming the logistics landscape.
It reinvents delivery tactics and provides a variety of use cases, such as peer-to-peer platforms, on-demand delivery, crowdshipping networks, locker-based solutions, and micro-fulfillment centers.
The advantages of this last mile strategy include cost-effectiveness, quick setup, environmental friendliness, and a customer-centric experience with often cheaper costs and more flexibility.
However, challenges like quality assurance, regulatory clarity, and trust and safety must be addressed for this trending delivery method to succeed.
Maintaining high service standards, overcoming legal challenges linked to contract drivers, and developing safe environments are all critical for businesses looking to try crowdsourced delivery services.
About The Author
Alina Kostukova
Skilled marketing content creator with a background in digital media and public relations. Focused on creating first-rate text and visual content that stands out and tells compelling stories.